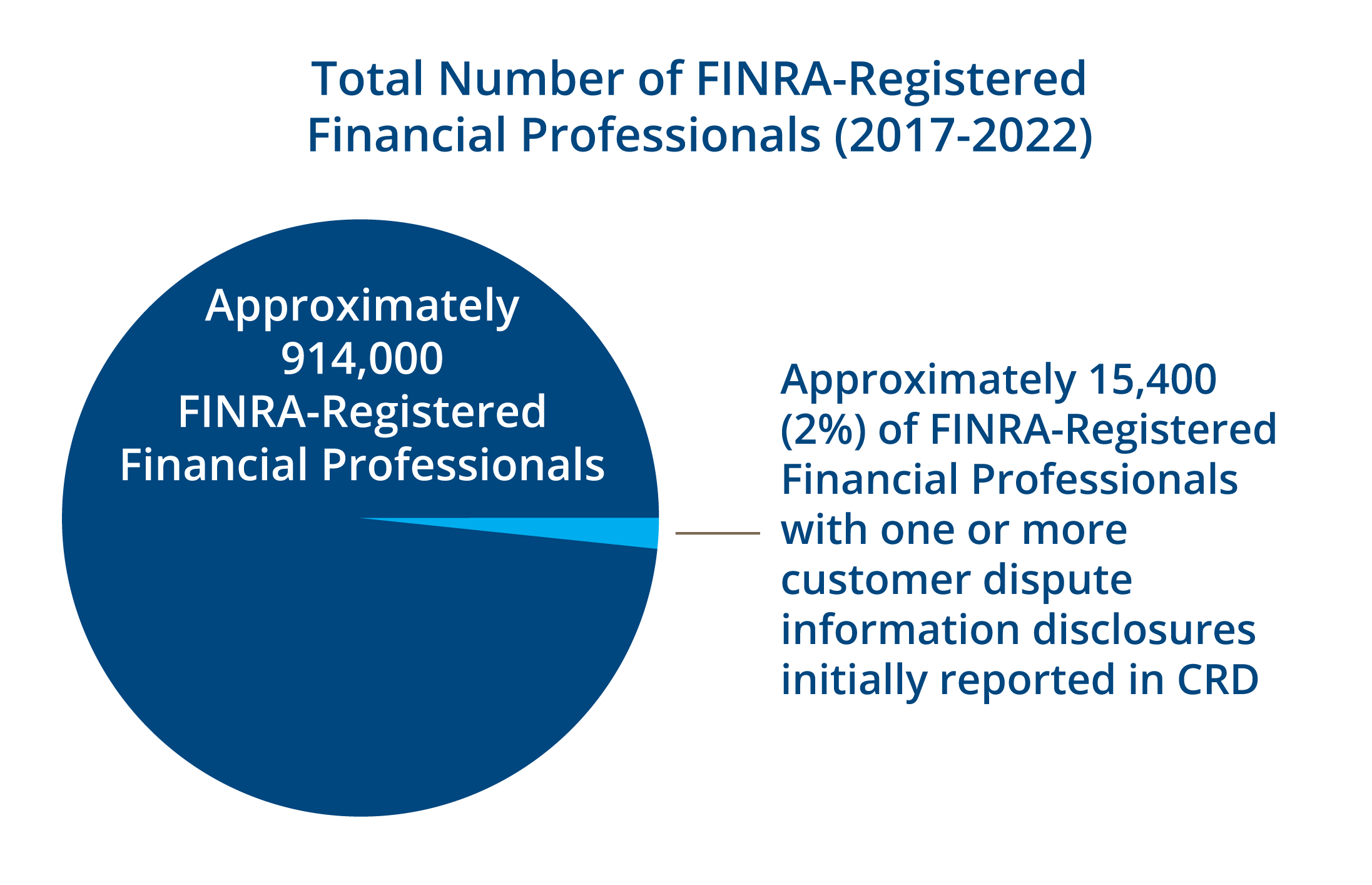
Background
FINRA operates the Central Registration Depository (CRD®), the central licensing and registration system used by FINRA, the SEC, other self-regulatory organizations, state securities regulators and firms. Uniform registration forms, including Forms U4, U5 and U6 are used by firms, associated persons and regulatory authorities to report registration information, which includes, among other things, administrative, regulatory, criminal history, financial and other information about associated persons, such as investment-related, customer-initiated arbitrations, civil litigations or customer complaints (i.e., customer dispute information).
The registration information, including customer dispute information, maintained in CRD serves three important purposes:
1. Regulators use CRD as an important source of regulatory information to inform registrations, examinations, investigations and disciplinary actions;
2. Firms use information in CRD for employment purposes; and
3. FINRA makes specific registration information collected in CRD publicly available through
BrokerCheck®, a free tool available on FINRA’s website to help investors make informed choices about the associated persons and firms with which they may conduct business.
How Expungement Works
Associated persons may seek to remove, or “expunge,” customer dispute information from CRD/BrokerCheck. FINRA Rules 12805 and 13805 specify a narrow set of circumstances in which expungement of customer dispute information from CRD is appropriate. To obtain an award containing expungement relief through the FINRA Dispute Resolution Services (DRS) arbitration forum, an independent arbitrator or a panel of independent arbitrators must determine that the party requesting expungement has established one of the narrow grounds in FINRA rules for expungement relief:
1. The claim, allegation or information is factually impossible or clearly erroneous;
2. The associated person was not involved in the alleged investment-related sales practice violation, forgery, theft, misappropriation or conversion of funds; or
3. The claim, allegation or information is false.
FINRA will expunge customer dispute information from CRD only if:
- FINRA receives a court order that directs expungement of the information; or
- A court confirms an arbitration award that authorizes such expungement.
Enhancements to the Expungement Process
Effective October 16, 2023, FINRA amended its rules to significantly enhance the expungement process.
An associated person seeking expungement of customer dispute information through arbitration must comply with the requirements of the Codes of Arbitration Procedure.
The enhancements to these rules set forth requirements specific to expungement requests made during each type of arbitration proceeding. These requirements include:
- Procedures for filing expungement requests;
- Requirements related to the composition, experience and responsibilities of the arbitrators deciding expungement requests;
- Procedures that arbitrators and participants must follow at expungement hearings;
- The required findings arbitrators must make to issue an award containing expungement relief; and
- Circumstances in which expungement requests are barred.
One of the most significant enhancements to the expungement process is that a Special Arbitrator Roster – a roster consisting of experienced public arbitrators, with additional expungement training – must decide straight-in requests. Straight-in requests are expungement requests that are filed under the Industry Code, rather than the Customer Code, against the member firm at which the person was associated at the time the customer dispute arose. Thus, the customer involved in the customer dispute is not a party to these requests. For these straight-in requests:
A panel of three arbitrators will be randomly selected from the Special Arbitrator Roster to decide the expungement request.
The parties cannot agree to fewer than three arbitrators to decide the expungement request.
The parties are prohibited from ranking and striking the arbitrators, stipulating to an arbitrator’s removal, or stipulating to the use of pre-selected arbitrators – the parties won’t have a say in who will decide the expungement request.
The three arbitrators must unanimously agree to award expungement based only on the narrow grounds specified in the rules, i.e., the claim, allegation or information is factually impossible, clearly erroneous, or false, or the associated person was not involved in the alleged misconduct.
Other significant enhancements include:
- Imposing strict time limits for seeking expungement in a straight-in request – e.g., DRS will deny the arbitration forum to an expungement request if the request is filed:
- more than two years after the close of the customer arbitration or civil litigation associated with the customer dispute information; or
- more than three years after the date the customer complaint was initially reported in CRD (if the customer complaint does not evolve into a customer arbitration or civil litigation).
- For any type of arbitration proceeding in which expungement is requested:
- requiring associated persons seeking expungement to appear in person or by video conference at the expungement hearing; and
- facilitating customer attendance and participation in all aspects of the expungement hearing and allowing customers to participate by telephone, in person or by video conference.
- Requiring notification to state securities regulators of expungement requests filed in the DRS arbitration forum, and for straight-in requests, providing a mechanism for state securities regulators to attend and participate in expungement hearings as a non-party in person or by video conference.